From Lions to Lemurs: Exploring the Fascinating Lists of Biota in Tanzania
Tanzania, a country nestled in East Africa, is a haven for nature enthusiasts and wildlife lovers. Its diverse landscapes, ranging from the iconic Serengeti plains to the majestic Mount Kilimanjaro, provide a home to an incredible variety of species. The biota of Tanzania refers to the total collection of living organisms found in the country, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. These biota have been meticulously cataloged in lists, which serve as invaluable resources for researchers, conservationists, and tourists alike.
What are lists of biota?
Lists of biota are comprehensive inventories that document the different species found within a particular region. In the case of Tanzania, these lists provide a detailed account of the rich biodiversity present in the country. They include information about the scientific names, common names, distribution, and conservation status of each species. These lists serve as a crucial reference for scientists studying ecosystems, as well as for policymakers developing conservation strategies.
Importance of lists of biota in Tanzania
The lists of biota in Tanzania play a crucial role in understanding and conserving the country’s unique natural heritage. By documenting the presence and distribution of various species, these lists enable scientists to identify areas of high biodiversity and prioritize conservation efforts. They also provide a baseline for monitoring changes in species populations over time, allowing researchers to assess the impact of human activities and climate change on Tanzania’s biota.
Furthermore, these lists are invaluable resources for ecotourism. Tourists visiting Tanzania can refer to these lists to identify the species they may encounter during their travels, enhancing their overall wildlife experience. The ability to showcase the incredible variety of species found in Tanzania not only attracts tourists but also raises awareness about the importance of conservation.
Endemic species in Tanzania
One of the most fascinating aspects of Tanzania’s biota is the presence of endemic species. Endemic species are those that are found exclusively within a particular geographic area and are not found anywhere else in the world. Tanzania is home to several remarkable endemic species, both flora and fauna.
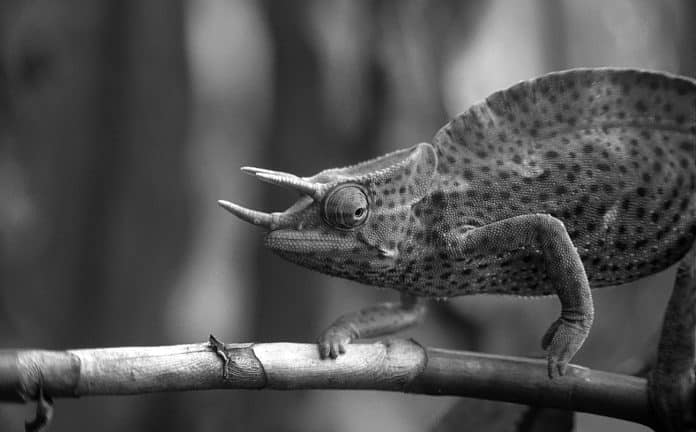
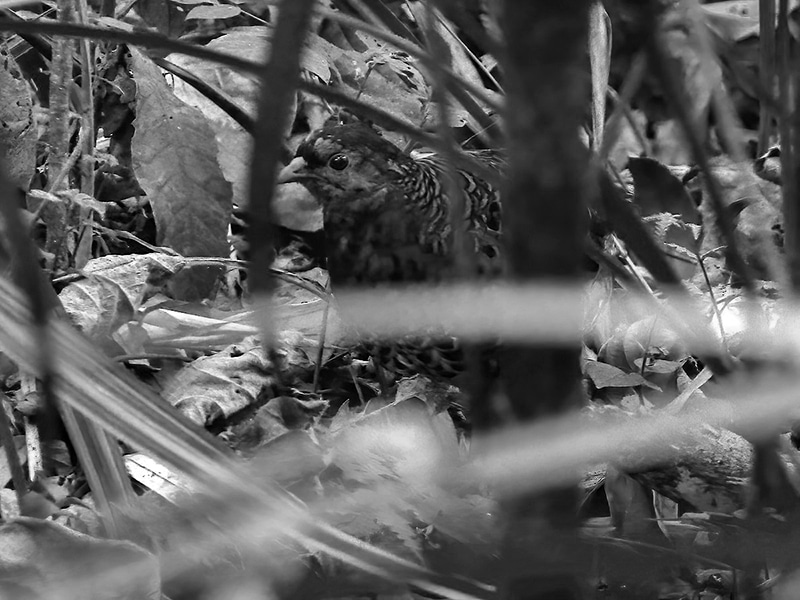
The Usambara three-horned chameleon (Trioceros deremensis) is a prime example of an endemic species in Tanzania. This extraordinary reptile, found only in the Usambara Mountains, is known for its unique ability to change colors and its distinctive three horns on its head. Another notable endemic species is the Udzungwa partridge (Xenoperdix udzungwensis), a critically endangered bird found solely in the Udzungwa Mountains. These endemic species serve as a testament to Tanzania’s biological distinctiveness and highlight the need for their protection.

Notable species in Tanzania
Beyond the endemic species, Tanzania boasts a remarkable array of charismatic wildlife. From the majestic African elephant to the agile cheetah, the country is home to some of the most iconic species on the planet. The Serengeti National Park, renowned for its annual wildebeest migration, is teeming with wildlife, including lions, leopards, giraffes, and zebras.
In the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, visitors can spot the critically endangered black rhinoceros, as well as the unique Maasai giraffe with its irregular spot pattern. The Ruaha National Park, the largest national park in Tanzania, is home to the African wild dog, a highly social and endangered carnivore. These notable species, among many others, contribute to the allure and fascination of Tanzania’s biota.
Flora and fauna diversity in Tanzania
Tanzania’s biota is not limited to its wildlife alone. The country’s diverse ecosystems support a wide range of plant species, making it a botanical paradise. From the towering baobab trees to the vibrant orchids, Tanzania’s flora captivates visitors with its beauty and ecological significance.
The Eastern Arc Mountains, a chain of ancient mountains in Tanzania, are recognized as one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots. These mountains are home to a staggering number of plant species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. The coastal forests of Tanzania are also rich in biodiversity, harboring unique plant species adapted to the challenging conditions of the coastal environment.
When it comes to fauna, Tanzania’s biota showcases an incredible variety of species. Apart from the iconic African mammals, the country is also home to a diverse array of bird species, reptiles, amphibians, and insects. The marine ecosystems along the Tanzanian coastline are particularly rich in marine life, with colorful coral reefs and abundant fish species.
Challenges in creating lists of biota in Tanzania
Creating comprehensive lists of biota in Tanzania is not without its challenges. The vastness of the country, coupled with its diverse landscapes, makes it a daunting task for researchers to survey and document every species. Remote and inaccessible regions, such as the dense forests of the Eastern Arc Mountains or the remote islands off the coast, pose logistical challenges for fieldwork.
Furthermore, the sheer number of species in Tanzania adds to the complexity of creating accurate lists. New species are constantly being discovered, and taxonomic revisions often lead to changes in species classifications. Additionally, language barriers and limited resources can hamper the efforts of local scientists and conservationists in contributing to the development of these lists.
Conservation efforts for the biota of Tanzania
Despite the challenges, Tanzania has made significant strides in conserving its biota. National parks, game reserves, and protected areas have been established throughout the country to safeguard critical habitats and species. The Tanzanian government, in collaboration with international organizations and local communities, has implemented various conservation initiatives.
Conservation efforts focus not only on protecting iconic species but also on promoting sustainable development and community engagement. Community-based conservation projects empower local communities to become stewards of their natural resources, ensuring the long-term protection of Tanzania’s biota. These efforts have not only contributed to the preservation of biodiversity but have also brought socio-economic benefits to local communities through ecotourism and sustainable resource management.
Future prospects for studying biota in Tanzania
As technology advances and scientific knowledge expands, the study of Tanzania’s biota holds great promise for the future. DNA sequencing techniques and remote sensing technologies are revolutionizing the field of biodiversity research, allowing scientists to unravel the intricacies of ecosystems and understand the relationships between species.
Collaboration between local and international researchers, as well as the involvement of citizen scientists, can further enhance the efforts to document and study Tanzania’s biota. The integration of traditional ecological knowledge with scientific research can provide a holistic understanding of the country’s diverse ecosystems.
Conclusion: Appreciating the rich biodiversity of Tanzania
In conclusion, the lists of biota in Tanzania provide a comprehensive overview of the country’s remarkable biodiversity. From endemic species to iconic wildlife, Tanzania’s biota captivates and inspires. By recognizing the importance of these lists and supporting conservation efforts, we can ensure the preservation of Tanzania’s natural heritage for future generations. So, pack your bags and embark on an unforgettable journey to discover the lions, lemurs, and countless other fascinating species that call Tanzania home. Let the lists of biota be your guide to exploring the wonders of this East African gem.
For more articles related to Wildlife in Tanzania (Animals), click here!

































