Pemba Island – History, Economy, Archaeology, Transport and More
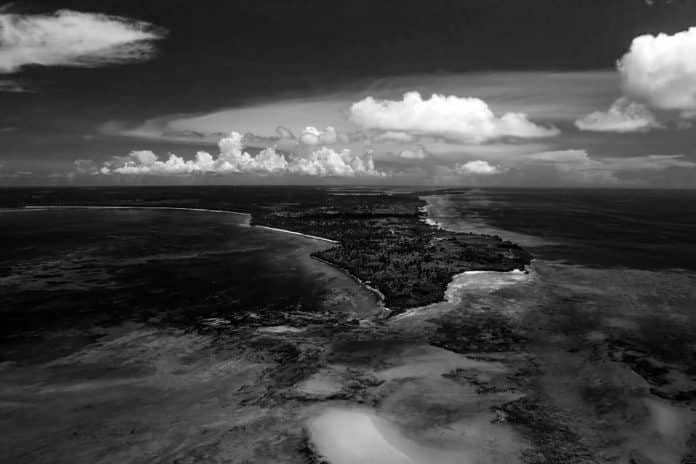
Pemba Island Africa in Swahili: means “Pemba kisiwa,” in Arabic: “الجزيرة الخضراء al-Jazīra al-khadrā,” meaning “The Green Island”; it is an island in Tanzanian which forms part of Zanzibar’s extension of islands, and lies within the Swahili shoreline in the beautiful Indian Ocean.
Pemba island is famous for its stunning coral reefs, clear turquoise waters, and vibrant marine life, making it a popular destination for snorkeling and scuba diving enthusiasts. Additionally, Pemba Island is known for its spice plantations, lush tropical forests, and pristine beaches, offering visitors a unique blend of adventure, relaxation, and cultural immersion.
Geography
With a surface area of 988 sq kilometers (381 sq miles), Pemba Island Zanzibar is located about 50 km [31 miles] northward of Unguja Island, the largest of the archipelago groups. In 1964, the Unity of Tanganyika and Zanzibar gave birth to Tanzania. It is situated 50 km east of the coast of Tanzania, just across the Pemba Passage. Bonded together with the Mafia islet (southwards of Unguja island), these two islands create the Spice Islets (not to be mistaken with the Maluku Budget of Indonesia). Farming predominates on most of the island, which is more hilly and fertile than Unguja. Cash crops such as cloves are produced in large quantities as well.
Pemba was hardly ever visited in years due to lack of roads and a neck for political savagery, except those who believe that the island was the center for witchcraft and traditional medicine collection. Migration has led to a significant Arab community presence on the island from Oman mixed with the original Swahili people. Also, a substantial majority of the inhabitants identify as Shirazi people.
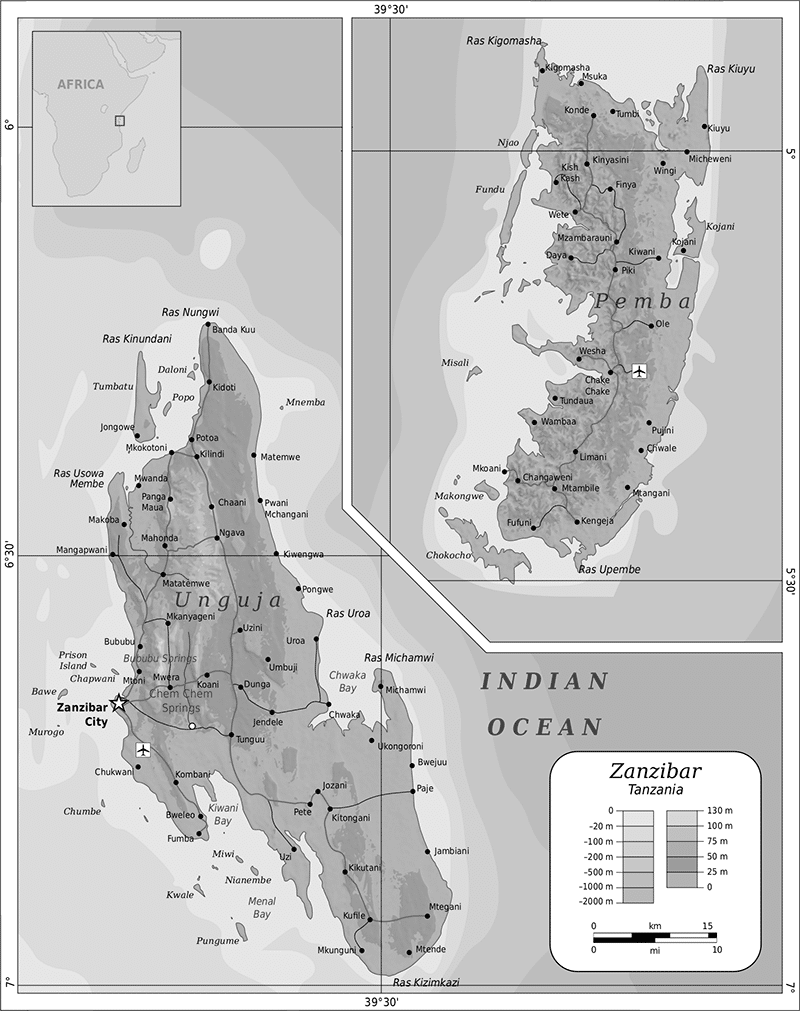
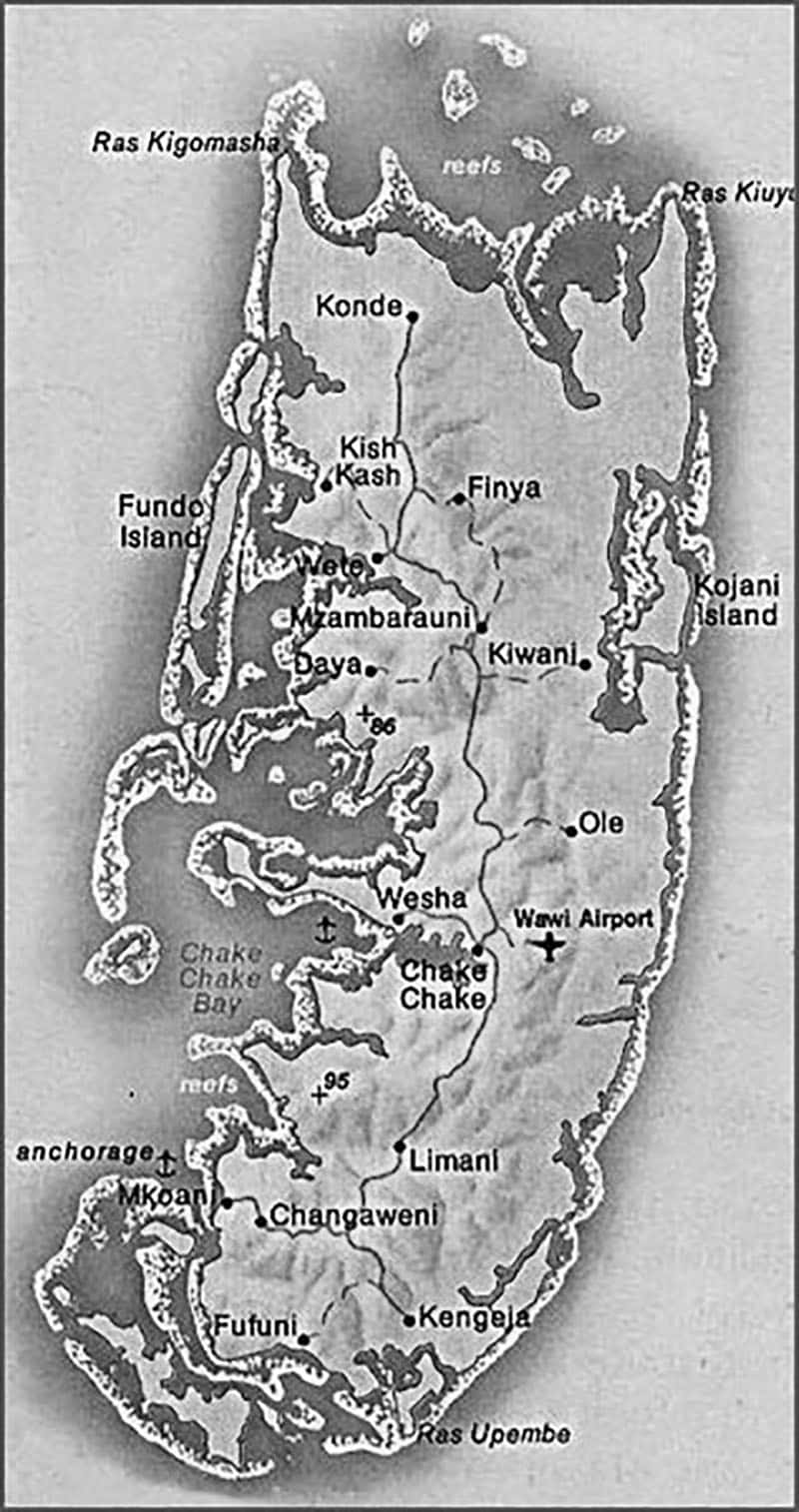
Pemba has the three most populous towns in the region: Chake-Chake [the Capital], Mkoani, and Wete, the largest city. On a mound, Chake-Chake sits overlooking a bay and the island of Misali, where the tides dictate when a rowboat can enter the local harbor. With exception for a narrow strip of land along its eastern coast, Pemba is a very fruitful place: in addition to clove trees, the people cultivate bananas, rice, coconut, and redish beans “called maharagwe’’ in Swahili.
Dive sites are abundant in Pemba, with steep drop-offs, untouched corals, and diverse marine life.
Important Bird Area
Birdlife International has recognized Pemba as an Important Bird Area [IBA] because it inhabits the green pigeons, scops owls, white –eye birds, and sunbirds on the islet
Climate
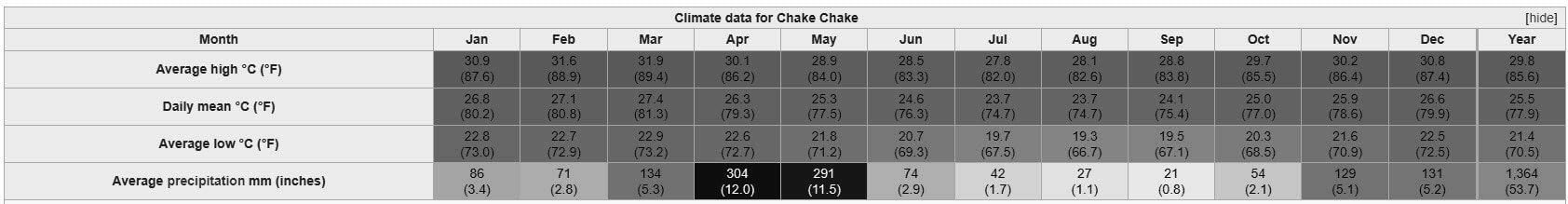
Tanzania’s mainland has a tropical climate, but Pemba’s is milder than Unguja island and tender than the mainland. The Köppen-Geiger climate system classifies this climate as “Aw.”. Chake Chake the Capital enjoys a typical summer temperature of 25.5 degrees Celsius (78 degrees Fahrenheit).
Rainfall is about 1,364 millimeters on average per year. The average temperature usually is between 24 – 27.4 degrees Celsius (75 °F – 81 °F) during the month. Between April and May are the rainiest months, while November and December bring more little rainfall. January through February are the driest months, and June through October are the longest.
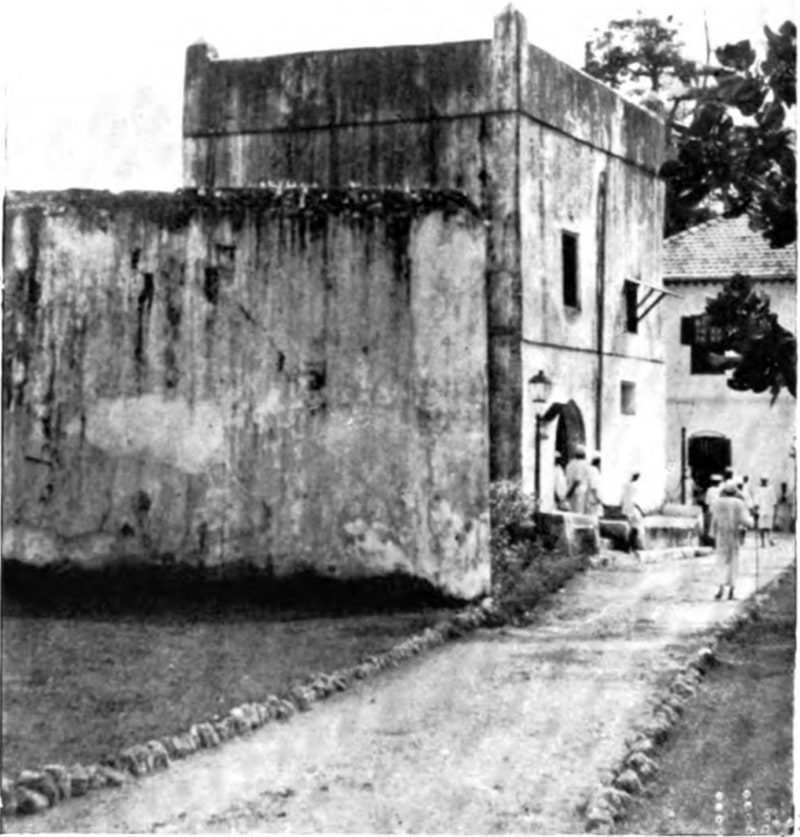
Archaeology
Archaeological survey on Pemba has brought to light its evenness and connection to the Swahili coastline trading system before 600 AD. On the northern coastlines, urban cities at Chwaka later evolved and flourished from the 11th century to 1500 AD.
Some of the best-preserved and early ruins on the Island “Ndagoni ruins,” probably around the 14th century, can be located just West of Pemba’s Capital, stretching along the Peninsula called Ras Mkumbuu.
One can see the Mkama Ndume ruins east of Chake-Chake, near Pujini village just south of the airport. With an easy drive from Chake-Chake Mkama Ndume or the airport. This fortification[Mkama Ndume Ruins] dates back to the fifteenth century on the Swahili coast.
History
According to a geographer of Arabic heritage Yakut, in the middle of the 13th century, two independent sultans ruled over parts of Pemba Islet.
In a statement provided to Reuters on 24 June 2016, Australia’s Minister for Transport, Infrastructure, and Regional Development, Darren Chester, said they found scraps from the missing Malaysia Airlines Plane 370 on Pemba island Tanzania.

Administration
Pemba is part of the semi-independent Revolutionary Regime of Zanzibar. It has two regions, namely North Pemba (Pemba Kaskazini) with Capital at Wete, and South Pemba (Pemba Kusini) with Capital at Mkoani. Although Chake Chake serves as Pemba’s Capital because it is closer to the airport and places host to both the High Court and the Presidential residence of the President of Zanzibar.
Economy
Fishing
Pemba is also significantly famous for its fertile fishing grounds. Between the mainland and the island is a total 50 kilometer deep Pemba Channel, which serves as the most significant fishing ground for game anglers on the Swahili coastline.
Farming and Agriculture
Except for a strip of land along its eastern coast, Pemba is ideal for global agriculture.
Cash Crops
A significant amount of Zanzibar export money comes from cloves production, with an enormous portion of clove trees in Zanzibar located on Pemba [3.5 million trees], due to better conditions on the island compared to Unguja island. Clove trees grow as high as 10- 15 meters tall and can last over 50 years of harvesting.
Farming predominates on most of the island, which is more hilly and fertile than Unguja. Pemba is a very fruitful place: in addition to clove trees, the locals grow bananas, rice, coconut, and red beans “called maharagwe in Swahili.” as well as cassava.
Land Surveying
A map with tourist guides and directions has been published by Chake-Chake’s Department of Surveys and Mapping since 1992 to promote tourism.
Transport – Pemba Island How to Get There
Airport
The cities of Arusha, Dar es Salaam, and Zanzibar City can be reached via Pemba Island Airport, also known as Wawi Airport or Karume Airport.
How to get from Zanzibar to Pemba island?
The easiest way to reach Pemba Island from Zanzibar is to take a place. There are multiple flights to Pemba island Tanzania. You can take flights Zanzibar to Pemba island by as little as $102.
How to get from Mombasa to Pemba island?
You can take a plane or a ferry to Pemba island from Mombasa.
How to get from Dar es salaam to Pemba island?
Getting to Pemba island from Dar es Salaam is easy. You can also travel by plane or ferry.
How to get from Arusha to Pemba Island?
You can take a plane from Arusha. There are plenty of flights from Pemba island to Arusha.
Pemba Island Weather
Pemba Island experiences a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. The island enjoys a wet season from April to June, with heavy rainfall and occasional tropical storms, while the dry season extends from July to March, offering pleasant and warm weather. Overall, Pemba Island’s weather is ideal for beach and water activities, with temperatures ranging from 25 to 35 degrees Celsius (77 to 95 degrees Fahrenheit).
Pemba Island People
The Pemba island population reaches 500,000, with rarely a couple of dozen foreigners.
The people of Pemba Island are primarily of Swahili and Arab descent, resulting in a diverse cultural heritage. They are known for their warm hospitality and friendly nature, welcoming visitors with open arms.
The local population relies largely on fishing, farming, and the cultivation of cloves, contributing to the island’s vibrant economy and way of life.
Pemba Island Tourism
Pemba Island offers a serene and untouched tropical getaway, where visitors can enjoy pristine beaches, vibrant marine life, and immerse themselves in the rich cultural heritage of the Swahili people.
Pemba island beaches
Pemba Island boasts stunning beaches with pristine white sands and crystal-clear turquoise waters. The island’s beaches offer a tranquil and picturesque setting, perfect for relaxation, sunbathing, and enjoying water activities such as swimming, snorkeling, and diving amidst vibrant coral reefs.
Pemba island diving
Pemba Island is renowned for its exceptional diving opportunities. With an abundance of coral reefs, colorful marine life, and excellent visibility, divers can explore underwater caves, drop-offs, and a variety of dive sites, making it a paradise for both beginner and experienced divers.
Pemba island fishing
Pemba Island is a haven for fishing enthusiasts, offering a rich fishing experience in its bountiful waters. Whether it’s deep-sea fishing or traditional handline fishing, visitors can enjoy the thrill of catching a variety of fish species, including marlin, sailfish, tuna, and snapper, while soaking in the island’s natural beauty.
Pemba island scuba diving
Pemba Island is a paradise for scuba diving enthusiasts, with its pristine coral reefs, abundant marine life, and excellent visibility. Divers can explore vibrant coral gardens, encounter a wide variety of tropical fish, and even have the chance to spot larger marine creatures like dolphins and turtles.
Pemba island snorkeling
Pemba Island offers fantastic snorkeling opportunities in its clear turquoise waters. Snorkelers can discover colorful coral reefs, swim alongside a diverse array of tropical fish, and witness the underwater beauty of this captivating island.
Pemba Island Hotels
There are multiple options for a Pemba island accommodation. If you’re looking for Pemba island holiday packages, check out this website!
Check out these amazing Pemba island Tanzania hotels:
The Manta resort Pemba island
Manta resort Pemba island is a luxurious and unique accommodation option known for its stunning underwater room. Manta resort Pemba island Tanzania offers guests the opportunity to stay in an exclusive floating suite where they can observe marine life from the comfort of their bedroom. With its beautiful surroundings, personalized service, and unforgettable underwater experience, Pemba island Tanzania manta resort is a top choice for those seeking an extraordinary and indulgent stay on Pemba Island.
Read more about manta hotel pemba island here:
Aiyana Pemba island
Aiyana Pemba Island is a boutique beach resort that offers a tranquil and secluded escape. With its private villas, pristine beaches, and breathtaking views of the Indian Ocean, this Pemba island hotel provides a serene and luxurious retreat for guests seeking relaxation and natural beauty.
Pemba Island is home to a unique and innovative Pemba island underwater room. The Pemba island resort underwater room allows guests to sleep surrounded by the vibrant marine life of the Indian Ocean. With its submerged bedroom and lounge area, the underwater hotel provides an unforgettable and immersive experience for those seeking an extraordinary stay in Pemba Island.
Read more about it here:
Fundu lagoon Pemba: islandFundu Lagoon on Pemba Island is a luxury beach resort nestled in a secluded and picturesque location . With its stylish accommodations, stunning beachfront setting, and a range of activities including diving and spa treatments, this Pemba island tanzania hotel offers an exclusive and idyllic retreat for those seeking a high-end tropical experience.
Visiting Pemba Island vs Zanzibar
Pemba Island and Zanzibar are both beautiful destinations in Tanzania, each with its own unique charm. Pemba Island is less developed and more secluded, offering pristine beaches, lush forests, and excellent diving spots.
It’s an ideal choice for those seeking a quieter and off-the-beaten-path experience. On the other hand, Zanzibar is more popular and developed, known for its vibrant culture, historic Stone Town, and a wide range of resorts, restaurants, and nightlife options. It attracts a larger number of tourists and offers a mix of relaxation and cultural exploration. Ultimately, the choice between Pemba Island and Zanzibar depends on personal preferences and travel goals.
FAQs
How to get to Pemba island from Zanzibar?
By plane is the best way to get to Pemba Island.
Is Pemba island safe?
While Pemba Island is generally considered safe for tourists, it is advisable to take common precautions to ensure a safe and enjoyable trip.
For more articles related to regions of Tanzania click here!

































